Table of Contents
ToggleCGPA Calculator – Calculate Your GPA, SGPA & Final CGPA Accurately
Last updated: December, 2025
A CGPA Calculator computes your Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) by following the standard CGPA grading system in Bangladesh. The essential CGPA formula is a credit-weighted average: the sum of (Grade Point × Credit Hours) for all completed semesters, divided by the total credit hours attempted. This calculation provides an accurate final CGPA out of a 4.0 scale.
Navigating the academic grading system in Bangladesh, particularly understanding and calculating your Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA), is crucial for every university student. Whether you’re tracking your semester progress or planning your final result, knowing how to find CGPA accurately is essential.
This comprehensive guide and tool explain the CGPA system in Bangladesh, details the credit-weighted GPA calculation , provides the necessary formulas, and serves as your authoritative resource—acting as both a definitive explainer and an essential CGPA Calculator tool.
Calculate your CGPA easily!
Custom Grade Scale
Your CGPA: 0.00
Total Credits Earned: 0.0
Summary Table
| Semester | Course | Grade | Point | Credits | Weighted Points |
|---|
These English learning programs are designed for students, job seekers, and professionals to build confidence in speaking, writing, and grammar—from basic to advanced level. Each course focuses on practical usage and real-life communication.
English Course List (Attractive & Professional)
- Spoken English + Grammar Smart Bundle
স্পোকেন ইংলিশের ফ্লুয়েন্সি ও গ্রামারের কনসেপ্ট একসাথে শক্ত করার কম্বো কোর্স। - ঘরে বসে Spoken English প্রোগ্রাম
ঘরে বসেই দৈনন্দিন কথোপকথনের জন্য প্র্যাকটিক্যাল স্পোকেন ইংলিশ শেখার কোর্স। - English Master Bundle (All-in-One Program)
Spoken, Grammar, Writing ও Vocabulary—সবকিছু একসাথে কাভার করা প্রিমিয়াম প্যাকেজ। - English Communication for Professionals
অফিস, মিটিং, প্রেজেন্টেশন ও ইমেইলের জন্য প্রফেশনাল ইংলিশ কমিউনিকেশন কোর্স। - English for Government Job Preparation
বিসিএস ও অন্যান্য সরকারি চাকরির ইংরেজি অংশের জন্য টার্গেটেড প্রস্তুতি কোর্স।
Prepare for IELTS with expertly designed programs that strengthen all four skills—Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking. These courses are ideal for students and professionals aiming for high scores and global opportunities.
IELTS Preparation Courses
- IELTS Live Interactive Batch
রিয়েল-টাইম অনলাইন ক্লাসে শিক্ষকের সঙ্গে সরাসরি ইন্টারঅ্যাকশন এবং দ্রুত ফলাফলের জন্য ইনটেনসিভ প্রস্তুতি। IELTS Reading & Listening Mock Tests
পরীক্ষার সময় সীমা ও বাস্তব পরীক্ষার ফরম্যাটে রিডিং ও লিসেনিং দক্ষতা বাড়ানোর জন্য ব্যাপক মক টেস্ট সিরিজ।
Explore trusted government and bank job preparation courses designed to strengthen core concepts and boost exam performance. Perfect for aspirants seeking structured, exam-focused learning for competitive success.
Government & Bank Job Preparation Courses
- BCS Preli Success Program – Recorded Course
বিসিএস প্রিলিমিনারির সম্পূর্ণ সিলেবাস কভার করা স্ট্র্যাটেজিক ও এক্সাম-ফোকাসড রেকর্ডেড প্রস্তুতি কোর্স। - Government Job Foundation Course (Basic to Advance)
সকল সরকারি চাকরির জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় বেসিক কনসেপ্ট, প্র্যাকটিস ও প্রস্তুতির শক্ত ভিত গড়ার কোর্স। - GK Mastery for Government Jobs
বিসিএস, ব্যাংক ও অন্যান্য সরকারি চাকরির জন্য জেনারেল নলেজের টার্গেটেড ও আপডেটেড প্রস্তুতি। - Bank Job Crack Program – Complete Preparation Course
ব্যাংক নিয়োগ পরীক্ষার জন্য গণিত, ইংরেজি, জিকে ও অ্যানালিটিক্যাল অংশের পূর্ণাঙ্গ ও স্মার্ট প্রস্তুতি।
These skill-development programs are designed for students, freelancers, and professionals to master high-demand digital, communication, and leadership skills. Each course focuses on practical learning for career growth and real-world application.
Professional & Freelancing Skill Courses
- Content Creation Bundle
ক্রিয়েটিভ কন্টেন্ট তৈরি, সোশ্যাল মিডিয়া মার্কেটিং ও ডিজাইন টুল ব্যবহার শেখার সম্পূর্ণ প্যাকেজ। - Email Marketing for Freelancing
ইমেইল মার্কেটিং কৌশল ও ক্যাম্পেইন ব্যবস্থাপনা শিখে অনলাইন আয়ের জন্য প্রস্তুতি। - Complete Professional Communication Bundle
প্রফেশনাল ইমেইল, মিটিং, প্রেজেন্টেশন ও কনফ্লিক্ট হ্যান্ডলিং-এর দক্ষতা বাড়ানোর কোর্স। - Smart Leadership Bundle
লিডারশিপ, টিম ম্যানেজমেন্ট ও প্রজেক্ট স্ট্র্যাটেজি শেখার জন্য বিশেষ প্রোগ্রাম। - Video Editing with Premiere Pro
ভিডিও এডিটিংয়ের সমস্ত কৌশল শিখে ক্রিয়েটিভ প্রজেক্ট তৈরি ও অনলাইন কন্টেন্ট তৈরি দক্ষতা অর্জন। - Communication Masterclass by Tahsan Khan
ভাষণ, কথোপকথন ও প্রেজেন্টেশনে আত্মবিশ্বাস বাড়ানোর জন্য বিশেষ মাস্টারক্লাস। - স্কিলসের দুনিয়ায় ঘুরে আসুন (Explore the World of Skills)
নতুন নতুন ডিমান্ডেড স্কিল সম্পর্কে জানার ও শেখার জন্য অনুপ্রেরণামূলক এক্সপ্লোরেশন প্রোগ্রাম।
What is CGPA?
Understanding the CGPA System in Bangladesh
The academic journey is marked by two key metrics: GPA and CGPA.
- GPA (Grade Point Average) or SGPA (Semester Grade Point Average): This is the grade average calculated for a single, specific academic period, usually one semester. It shows your performance in that specific term.
- CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average): This is the overall average grade point achieved across all completed semesters of a degree program. It is the final official academic measurement used for transcripts and employment.
The entire CGPA system in Bangladesh is generally based on a credit-weighted evaluation model. This means that courses with more allocated credit hours (typically major or intensive subjects) have a larger impact on your GPA and subsequent CGPA than courses with fewer credits.
For baseball fans and players, this ERA Calculator helps you quickly compute your Earned Run Average with precision.
GPA & CGPA Grading System in Bangladesh
Most public and private universities in Bangladesh utilize a standardized grading structure based on a 4.0 scale for calculating GPA and CGPA. This generalized GPA grading system in Bangladesh maps a student’s numerical marks to a specific letter grade and an associated Grade Point.
Generalized Grade-to-Point Table
While minor variations exist, the following table represents the widely adopted CGPA grading system used by the majority of higher education institutions in the country.
| Numerical Equivalent (Marks) | Letter Grade | Grade Point | Remarks |
| 80% and above | A+ | 4 | Excellent |
| 75% to less than 80% | A | 3.75 | Very Good |
| 70% to less than 75% | A- | 3.5 | Very Good |
| 65% to less than 70% | B+ | 3.25 | Good |
| 60% to less than 65% | B | 3 | Good |
| 55% to less than 60% | B- | 2.75 | Satisfactory |
| 50% to less than 55% | C+ | 2.5 | Pass |
| 45% to less than 50% | C | 2.25 | Pass |
| 40% to less than 45% | D | 2 | Pass |
| Less than 40% | F | 0 | Failure |
Academic Note: Always consult your official university academic regulations for the precise GPA grading system in Bangladesh used by your institution, as some may use a straight point system (e.g., 4.0 for 80% and above, 3.0 for 70-79%, etc.).
Wondering if you can dunk? Find out your vertical jump requirements with this fun and detailed Dunk Calculator.
How to Calculate CGPA (Step-by-Step Guide)
To reliably calculate CGPA and accurately predict your results, you must follow the credit-weighted calculation logic
1. The Credit-Weighted Formula
The formula ensures that the final result reflects the importance of each course based on its credit load.

This formula is used for calculating both the SGPA (for one semester) and the CGPA (cumulatively across all semesters).
2. Step-by-Step Calculation for SGPA (Example 1)
Let’s illustrate how to calculate CGPA for a single semester (SGPA).
| Course Name | Credit Hours (Ci) | Letter Grade | Grade Point (GPi) | GP × Credits (GPi×Ci) |
| Physics I | 3 | A+ | 4 | 4.00×3.0=12.00 |
| Mathematics I | 3 | B+ | 3.25 | 3.25×3.0=9.75 |
| English | 2 | A- | 3.5 | 3.50×2.0=7.00 |
| Workshop | 1.5 | B | 3 | 3.00×1.5=4.50 |
| Totals | ∑Ci=9.5 | ∑(GPi×Ci)=33.25 |
Using the formula:

3. Step-by-Step Calculation for Final CGPA (Example 2)
This example shows how to find CGPA cumulatively by combining results from two full semesters (SGPA → Final CGPA).
| Semester | SGPA Achieved | Total Credit Hours Completed in Semester (CTotal) | Total Grade Points Earned (SGPA×CTotal) |
| Semester 1 | 3.499 | 15 | 3.499×15.0=52.485 |
| Semester 2 | 3.75 | 18 | 3.750×18.0=67.500 |
| Totals | ∑CTotal=33.0 | ∑(SGPA×CTotal)=119.985 |
CGPA Calculation:
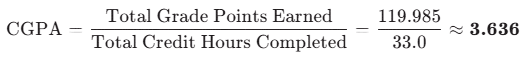
This result, 3.636, is your final CGPA after two semesters.
Semester GPA (SGPA) → Final CGPA
The final CGPA is simply the aggregated result of all SGPAs achieved throughout the program, weighted by the total credit hours attempted in each respective semester. This is the core logic applied by any effective Semester CGPA calculator.
How to calculate CGPA out of 4
The grading system in Bangladesh is inherently a 4.0 scale. When you use the credit-weighted formula, the maximum possible result is 4.00. Therefore, the calculation naturally ensures your result is computed out of 4, making the process straightforward for local and international standard referencing.
Common Mistakes Students Make
- Ignoring Credit Weighting: Simply averaging SGPAs without multiplying by the total semester credit hours will lead to an incorrect CGPA.
- Confusing GPA vs. CGPA: Mistaking a single semester result (GPA/SGPA) for the cumulative degree result (CGPA).
- Including Failed Courses Incorrectly: Always include the grade point (0.00) and credit hours of any failed course (F grade) in the calculation until it is successfully repeated and a passing grade is achieved.
How to Calculate CGPA Using the Tool
Our tool is designed for maximum speed and accuracy on any device.
- Select Your Preset (University/Program): Use the drop-down menu to select your institution (e.g., National University, Public University, Private University, or Custom). This automatically loads the correct grading scale and, where applicable, the retake logic.
- Choose Term Mode: Toggle between Semester, Trimester, or Year mode based on your program’s structure. Then, specify the total number of terms you have completed or plan to calculate (e.g., 8 semesters for a 4-year Honours degree).
- Input Credits & Grades: For each course in each term: enter the course Credit (e.g., 3.0, 4.0, or 1.5 for labs) and the Letter Grade you achieved. You must enter all credits in the denominator to get the correct weighted average. The system offers live validation and warns you if credits are missing.
- Review SGPA & Cumulative CGPA: Your SGPA for the current term and your total CGPA will update live on the sticky summary card located on the right (or at the top on mobile). Review the detailed breakdown of “Earned Points” for full transparency.
- Export, Or Print: Use the One-Click Export button to generate a clean, print-friendly PDF of your results, or Print a clear copy.
CGPA to Percentage Conversion
A common student query is the translation of CGPA into a percentage score.
Disclaimer: Most universities in Bangladesh do not officially issue a percentage equivalent on the academic transcript. The CGPA itself is the final academic metric.
However, several common (but unofficial) rules of thumb are used for external requirements, such as international applications or certain job sectors:
| Conversion Method | Formula | Notes |
| Standard Rule (Common) | Percentage = CGPA × 25 | Used widely for quick estimation. Example: 3.50×25=87.5% |
| Alternate Rule | Percentage = (CGPA × 20) + 20 | Used by some institutions in South Asia. Example: (3.50×20)+20=90% |
Crucial Academic Warning: Do not rely on these formulas for official purposes. Always clarify with the requesting organization (e.g., employer, foreign university) which conversion method they accept, or simply provide your official CGPA.
CGPA Calculator BD vs GPA Calculator BD
The names highlight the primary function:
- GPA calculator bd (or SGPA calculator) is designed specifically to calculate the result of one single semester only.
- CGPA calculator bd is designed to calculate the cumulative average over multiple semesters or the entire program.
A good CGPA Calculator should ideally function as both, allowing users to input one semester’s data for SGPA, or multiple semesters’ data for the cumulative CGPA.
Honours CGPA Calculator: Accounting for 4 Years
A typical Honours degree in Bangladesh spans four academic years, resulting in approximately 8 to 12 total semesters (including practical and thesis components).
When using an honours cgpa calculator, you need to ensure the tool allows you to input grades and credits for all completed semesters. This means calculating the total credit points earned from all 4 years and dividing them by the total attempted credit hours, according to the main formula.
Semester CGPA Calculator (Multi-Semester Input)
An advanced Semester CGPA calculator or online tool facilitates multi-semester input. Instead of calculating SGPA semester by semester and then combining them manually, the tool should allow you to:
- Input the total credits and SGPA from previously completed semesters.
- Input the current semester’s courses, grades, and credits.
- Combine all data instantly to yield the updated cumulative CGPA.
This functionality is what separates a basic GPA tool from a robust, continuous Semester CGPA calculator.
Related Academic Calculators
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About CGPA Calculation
The fastest way is to use a dedicated CGPA Calculator tool, enter your course grades and credit hours for all completed semesters, and let the tool automatically apply the credit-weighted formula.
While most follow the 4.0 scale and credit-weighted logic, small differences exist, especially in the mark ranges for specific letter grades (e.g., 80% vs 75% for A+), and the policies regarding course retakes or failed courses.
Yes. A GPA calculator BD calculates one semester's result (SGPA), while a CGPA calculator BD calculates the overall cumulative average of all semesters completed.
The formula used to calculate CGPA out of 4 is the credit-weighted average: (GP × Credits) / ∑ (Total Credits). Since the maximum Grade Point is 4.00, the maximum result is 4.00.
There is no single official method for CGPA to percentage conversion recognized by all institutions. You should use the official CGPA and provide the conversion rule (like CGPA × 25) only if explicitly requested by a third party.
Yes, any reliable tool or method used to calculate your Honours CGPA calculator must include the grades and credit hours from all 8 to 12 semesters of your four-year program.
You combine results by multiplying each semester's SGPA by its total credit hours. Sum these Grade Points, and divide by the total cumulative credit hours attempted. This is the function of a Semester CGPA calculator.
The CGPA system discussed here primarily applies to university-level (Honours/Masters) education. Grading systems for HSC/SSC (Higher Secondary/Secondary) may differ, often using a 5.0 scale.
All credit hours for courses officially listed on your academic transcript, including any repeated courses (with the final passing grade), must be included when learning how to find CGPA.
The most important factor in the GPA grading system in Bangladesh is the credit hour of a course, as it determines the weight of that course in your final CGPA.
Privacy & Data Handling
Your privacy is paramount. This CGPA Calculator BD runs entirely within your web browser.
No Data Stored: The grades, credits, and results you enter are not stored on our servers. When you close your browser or click “Reset,” the data is cleared.
Security: This ensures complete data privacy and security for all users.
Disclaimer & Academic Notes
Academic Disclaimer: This CGPA Calculator guide and the accompanying formulas are intended solely for academic guidance, estimation, and informational purposes.
- The official academic transcript issued by your university is the final and definitive authority for all your academic records.
- Grading rules, credit systems, and CGPA policies may vary significantly by institution within Bangladesh.
Users must verify their specific university’s policies and regulations (e.g., public university guidelines, official Bangladesh university grading policies) to ensure calculation accuracy.
References
The CGPA Calculator is built upon the foundational policies of the following high-authority documents:
